Ansible Tower Installation and Configuration Guide
Overview
In this article we will setup and configure Ansible Tower on Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL). By now unless you are hiding under a rock, you have heard about Ansible. Ansible is quickly becoming the standard automation language used in enterprises for automating everything. Ansible is powerful, simple, easy to learn and these of course are the main reasons it becoming the standard everywhere. Ansible has two components: Ansible core and Ansible Tower. Core provides the Ansible runtime that executes playbooks (yaml files defining tasks and roles) against inventories (group of hosts). Ansible Tower provides management, visibility, job scheduling, credentials, RBAC, auditing / compliance and more. Installing Ansible Tower also installs Ansible core so you kill two birds with one stone.
Prerequisites
Before starting you need to deploy a host or VM with RHEL 7.3. Once the host is configured and on the network, you can register it with subscription-manager and enable the required repositories. For Ansible Tower you need rhel-7-server-rpms, rhel-7-server-extras-rpms and EPEL.
# subscription-manager register
# subscription-manager list --available
# subscription-manager attach --pool=<pool id>
# subscription-manager repos --disable=*
# subscription-manager repos --enable=rhel-7-server-rpms \ --enable=rhel-7-server-extras-rpms
Install and configure EPEL repositories.
yum install http://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-7.noarch.rpm
Install Ansible
# yum install -y ansible
Install Ansible Tower
Download latest Ansible Tower release.
# curl -k -O https://releases.ansible.com/awx/setup/ansible-tower-setup-latest.tar.gz
Extract tarball.
# gunzip ansible-tower-setup-latest.tar.gz
# tar xvf ansible-tower-setup-latest.tar
Configure Ansible Tower. Ansible Tower uses an Ansible playbook to deploy itself (what a great idea). As such configuration parameters or groupvars are stored in inventory file.
# cd ansible-tower-setup-3.1.2
# vi inventory [tower] localhost ansible_connection=local [database] [all:vars] admin_password='redhat01' pg_host='' pg_port='' pg_database='awx' pg_username='awx' pg_password='redhat01' rabbitmq_port=5672 rabbitmq_vhost=tower rabbitmq_username=tower rabbitmq_password='redhat01' rabbitmq_cookie=cookiemonster # Needs to be true for fqdns and ip addresses rabbitmq_use_long_name=false
Run Setup.
# ./setup.sh
Configure Ansible Tower
Ansible Tower Provides a RESTful API, CLI and UI. To connect to the UI simply open browser using https and point to your Ansible Tower IP or hostname.
https://<Ansible Tower IP or Hostname>
Login using the user you configured in the inventory file, in this case admin/redhat01.
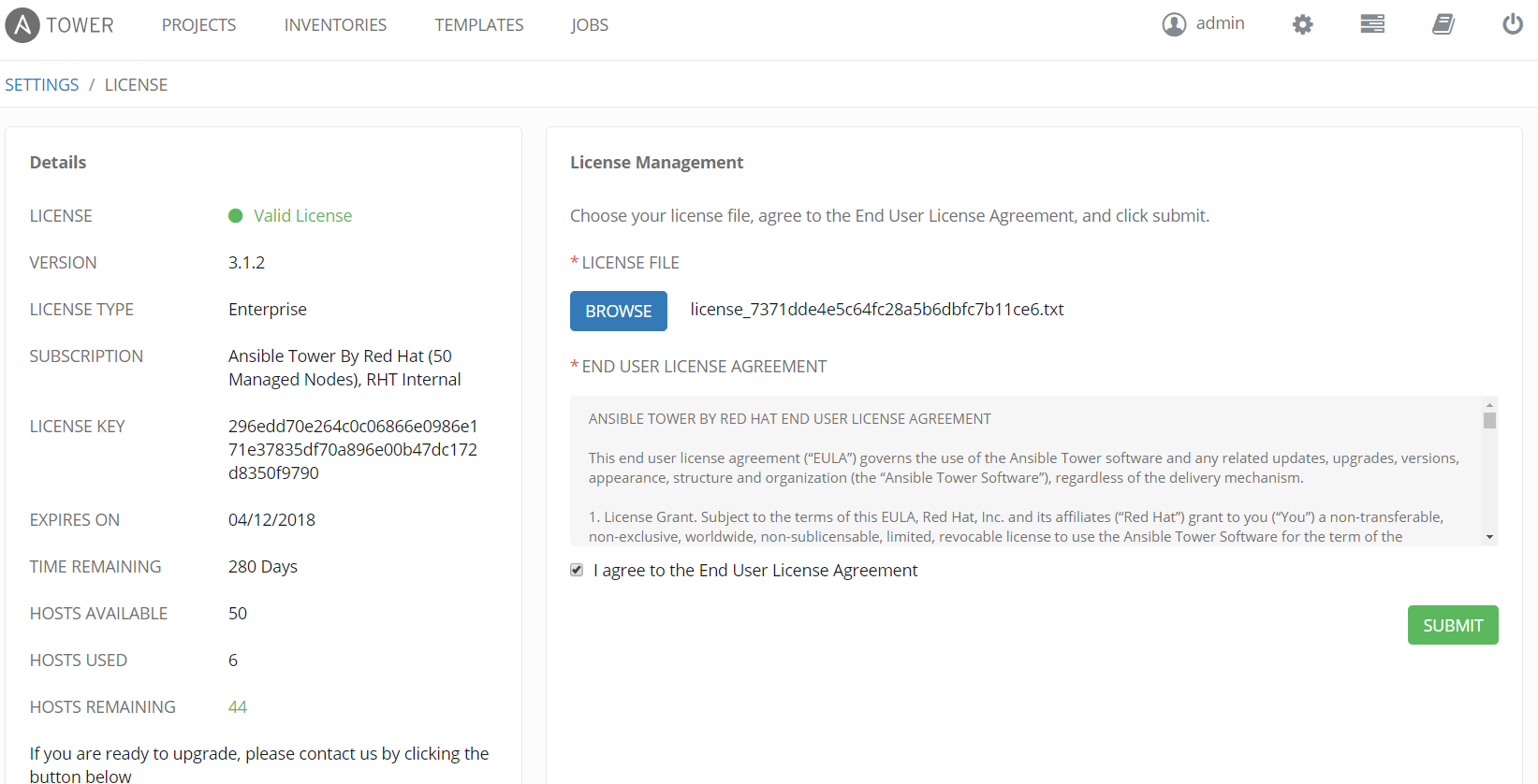
Once you are logged in, you need to configure license. Tower license comes in a file, so simply browse to the file and accept the terms. If you don't have a license you can get a trial here.
Summary
In this brief article we went through how to install and configure Ansible Tower. Regardless of if you are new to Ansible or experienced, Tower is definitely worth looking at as it provides a solid management platform for Ansible and makes everything even easier and more powerful!
Happy Ansibleling!
(c) 2017 Keith Tenzer

