Getting Started with Volume Snapshots in OpenShift 4 and OpenShift Container Storage



Overview
Volume snapshots are the ability to create snapshots of persistent volumes in kubernetes using the container storage interface (csi) driver. The csi driver allows storage solutions to integrate into kubernetes and expose their technologies. Snapshots of course, have been and are a key technology when discussing data workloads because they enable backup/restore seamlessly, on-demand and in a split second. Even though volume snapshots are in the alpha stage, several storage providers already have integrations, including one that is very interesting, Ceph RDB.
Ceph is a software-defined storage platform that is rock solid, very mature and provides file, block as well as object storage. In this case we will using block storage. In Ceph block is provided through rbd (Rados Block Device). A container-native storage solution called Rook, based completely on kubernetes operators provides a container-native deployment of Ceph on Kubernetes or OpenShift. In this article we are using OpenShift 4.2 GA and a internal beta release of OpenShift Container Storage (based on Rook).
How it Works
The CSI driver allows for a snapshotter to be implemented. The snapshotter runs as a side-car container and watches the kubernetes API for snapshot related events from the CSI driver. In order to create a volume snapshot a volume snapshot class must exist. This is similar to the storage class but defines the snapshotter and access to the appropriate CSI driver. Once a volume snapshot class exists a volume snapshot can be created for a given persistent volume claim (pvc). The volume snapshot will then trigger the snapshot operation on the storage device, in this case Ceph RBD. The volume snapshot allows the snapshotter to provide metadata about the snapshot contents to the end-user.
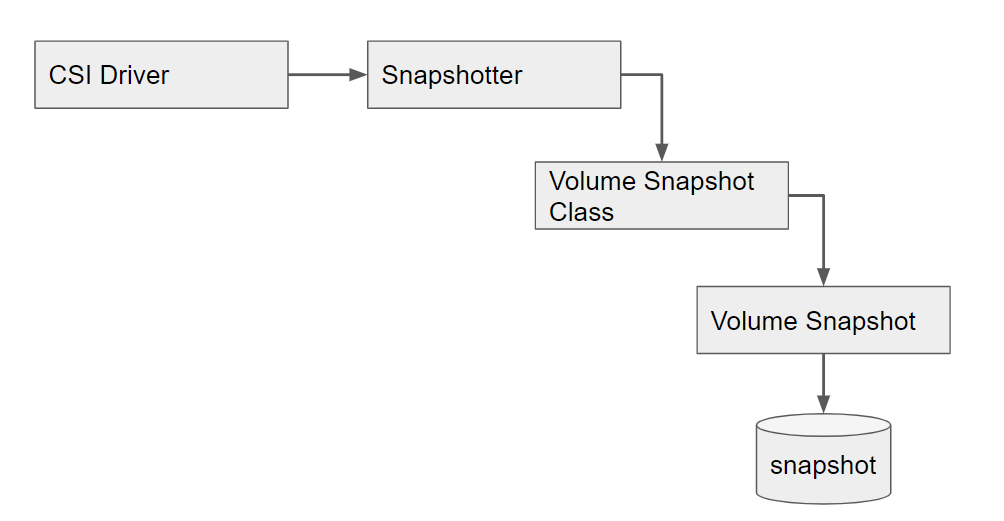
Volume Snapshot Backup
Now that we understand the basics we will see how to actually create a backup. We will deploy a mariadb database on persistent storage using Ceph RBD, create a table in the database with some records, setup a volume snapshot class and finally perform a volume snapshot of the database.
Deploy Mariadb database
We deployed a persistent mariadb database using ceph rbd provisioner.

Add table and records to database
Connect to database.
$ oc rsh -n databases mariadb-6-rswv6
sh-4.2$ mysql -u root Welcome to the MariaDB monitor. Commands end with ; or \g. Your MariaDB connection id is 20 Server version: 10.2.22-MariaDB MariaDB Server Copyright (c) 2000, 2018, Oracle, MariaDB Corporation Ab and others. Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.
MariaDB [(none)]> use sampledb;
Create table authors and add some records.
MariaDB [(none)]> CREATE TABLE authors (id INT, name VARCHAR(20), email VARCHAR(20)); MariaDB [(none)]> INSERT INTO authors (id,name,email) VALUES(1,"Keith","keith@domain.com"); MariaDB [(none)]> INSERT INTO authors (id,name,email) VALUES(2,"John","john@domain.com"); MariaDB [(none)]> INSERT INTO authors (id,name,email) VALUES(3,"Bob","bob@domain.com");
Show records for table authors.
MariaDB [books]> select * from authors; +------+-------+-----------------+ | id | name | email | +------+-------+-----------------+ | 1 | Keith | keith@domain.com| | 2 | John | john@domain.com | | 3 | Bob | bob@domain.com | +------+-------+-----------------+ 3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
Get the Ceph RBD Image
First get the persistent volume name for our mariadb.
$ oc get pv -o 'custom-columns=NAME:.spec.claimRef.name,PVNAME:.metadata.name,STORAGECLASS:.spec.storageClassName,VOLUMEHANDLE:.spec.csi.volumeHandle' NAME PVNAME STORAGECLASS VOLUMEHANDLE ocs-deviceset-0-0-cc8nr pvc-08b360c9-0214-11ea-a05b-005056814c6f thin <none> ocs-deviceset-1-0-bntqm pvc-08b53c69-0214-11ea-a05b-005056814c6f thin <none> ocs-deviceset-2-0-g65tl pvc-08b70a3e-0214-11ea-a05b-005056814c6f thin <none> db-noobaa-core-0 pvc-27708237-0214-11ea-a05b-005056814c6f ocs-storagecluster-ceph-rbd 0001-0011-openshift-storage-0000000000000001-2f81ea18-0214-11ea-aa51-0a580a81000d rook-ceph-mon-a pvc-9dd37deb-0213-11ea-a05b-005056814c6f thin <none> rook-ceph-mon-b pvc-a12c254a-0213-11ea-a05b-005056814c6f thin <none> mariadb pvc-a370d1ed-021b-11ea-bca7-005056818b87 ocs-storagecluster-ceph-rbd 0001-0011-openshift-storage-0000000000000001-a380eb7b-021b-11ea-aa51-0a580a81000d rook-ceph-mon-c pvc-a42a79c9-0213-11ea-a05b-005056814c6f thin
Next get the Ceph rbd image mapped to our persistent volume.
[ktenzer@keith-laptop ~]$ oc get pv pvc-a370d1ed-021b-11ea-bca7-005056818b87 -o jsonpath='{.spec.csi.volumeHandle}' | cut -d '-' -f 6- | awk '{print "csi-vol-"$1}'
csi-vol-a380eb7b-021b-11ea-aa51-0a580a81000d
Create Volume Snapshot Class
In order to create the volume snapshot class some information is needed. We need to know the snapshotter, the provisioner secret and the secret namespace.
$ oc get sc ocs-storagecluster-ceph-rbd -o yaml
apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1
kind: StorageClass
metadata:
creationTimestamp: "2019-11-08T10:35:52Z"
name: ocs-storagecluster-ceph-rbd
ownerReferences:
- apiVersion: ocs.openshift.io/v1
blockOwnerDeletion: true
controller: true
kind: StorageCluster
name: ocs-storagecluster
uid: 893852b9-0213-11ea-bca7-005056818b87
resourceVersion: "30740"
selfLink: /apis/storage.k8s.io/v1/storageclasses/ocs-storagecluster-ceph-rbd
uid: 89666c5f-0213-11ea-bab7-00505681830f
parameters:
clusterID: openshift-storage
csi.storage.k8s.io/fstype: ext4
csi.storage.k8s.io/node-stage-secret-name: rook-csi-rbd-node
csi.storage.k8s.io/node-stage-secret-namespace: openshift-storage
csi.storage.k8s.io/provisioner-secret-name: rook-csi-rbd-provisioner
csi.storage.k8s.io/provisioner-secret-namespace: openshift-storage
imageFeatures: layering
imageFormat: "2"
pool: ocs-storagecluster-cephblockpool
provisioner: openshift-storage.rbd.csi.ceph.com
reclaimPolicy: Delete
volumeBindingMode: Immediate
Create volume snapshot class.
$ vi snapshot-class.yaml apiVersion: snapshot.storage.k8s.io/v1alpha1 kind: VolumeSnapshotClass metadata: name: ocs-storagecluster-ceph-rbd-snapshot snapshotter: openshift-storage.rbd.csi.ceph.com parameters: clusterID: openshift-storage csi.storage.k8s.io/snapshotter-secret-name: rook-csi-rbd-provisioner csi.storage.k8s.io/snapshotter-secret-namespace: openshift-storage
$ oc apply -f snapshot-class.yaml
Create Volume Snapshot
Now that we have our volume snapshot class we can snapshot a persistent volume claim.
$ vi create-snapshot.yaml
apiVersion: snapshot.storage.k8s.io/v1alpha1
kind: VolumeSnapshot
metadata:
name: mariadb-1
spec:
snapshotClassName: ocs-storagecluster-ceph-rbd-snapshot
source:
name: mariadb
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
$ oc apply -f create-snapshot.yaml -n databases
Show volume snapshot.
[ktenzer@keith-laptop ~]$ oc get volumesnapshot NAME AGE mariadb-1 35s
Show the volume snapshot content. The snapshotter provides metadata about snapshots to kubernetes and stores that information in the snapshot content.
$ oc get volumesnapshotcontent NAME AGE snapcontent-fdf13bf1-0221-11ea-bab7-00505681830f 3m2s
$ oc get volumesnapshotcontent snapcontent-fdf13bf1-0221-11ea-bab7-00505681830f -o yaml
apiVersion: snapshot.storage.k8s.io/v1alpha1
kind: VolumeSnapshotContent
metadata:
creationTimestamp: "2019-11-08T12:19:22Z"
finalizers:
- snapshot.storage.kubernetes.io/volumesnapshotcontent-protection
generation: 1
name: snapcontent-fdf13bf1-0221-11ea-bab7-00505681830f
resourceVersion: "74329"
selfLink: /apis/snapshot.storage.k8s.io/v1alpha1/volumesnapshotcontents/snapcontent-fdf13bf1-0221-11ea-bab7-00505681830f
uid: fef777ae-0221-11ea-a05b-005056814c6f
spec:
csiVolumeSnapshotSource:
creationTime: 1573215562000000000
driver: openshift-storage.rbd.csi.ceph.com
restoreSize: 1073741824
snapshotHandle: 0001-0011-openshift-storage-0000000000000001-fe517800-0221-11ea-aa51-0a580a81000d
deletionPolicy: Delete
persistentVolumeRef:
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolume
name: pvc-a370d1ed-021b-11ea-bca7-005056818b87
resourceVersion: "55833"
uid: a3ef7f08-021b-11ea-bab7-00505681830f
snapshotClassName: ocs-storagecluster-ceph-rbd-snapshot
volumeSnapshotRef:
apiVersion: snapshot.storage.k8s.io/v1alpha1
kind: VolumeSnapshot
name: mariadb-1
namespace: databases
resourceVersion: "74316"
uid: fdf13bf1-0221-11ea-bab7-00505681830f
Verify Snapshot on Ceph RBD
OpenShift Container Storage provides a tools pods for easily accessing the Ceph cluster. Save the pod name to a vairable.
TOOLS_POD=$(oc get pods -n openshift-storage -l app=rook-ceph-tools -o name)
Using tools pod show information about mariadb Ceph rbd image.
$ oc rsh -n openshift-storage $TOOLS_POD rbd -p ocs-storagecluster-cephblockpool info csi-vol-a380eb7b-021b-11ea-aa51-0a580a81000d rbd image 'csi-vol-a380eb7b-021b-11ea-aa51-0a580a81000d': size 1 GiB in 256 objects order 22 (4 MiB objects) snapshot_count: 0 id: 5617782da596 block_name_prefix: rbd_data.5617782da596 format: 2 features: layering op_features: flags: create_timestamp: Fri Nov 8 11:33:52 2019 access_timestamp: Fri Nov 8 11:33:52 2019 modify_timestamp: Fri Nov 8 11:33:52 2019
List all snapshots for mariadb Ceph rbd image.
$ oc rsh -n openshift-storage $TOOLS_POD rbd snap ls ocs-storagecluster-cephblockpool/csi-vol-a380eb7b-021b-11ea-aa51-0a580a81000d
SNAPID NAME SIZE PROTECTED TIMESTAMP
6 csi-snap-fe517800-0221-11ea-aa51-0a580a81000d 1 GiB yes Fri Nov 8 12:19:22 2019
Volume Snapshot Restore
Now that we have performed and validated a backup lets do a restore. We will drop the table to simulate a loss of data and then perform a restore from our snapshot and hopefully get access to our data again.
Connect to database
$ oc rsh -n databases mariadb-6-rswv6
sh-4.2$ mysql -u root Welcome to the MariaDB monitor. Commands end with ; or \g. Your MariaDB connection id is 20 Server version: 10.2.22-MariaDB MariaDB Server Copyright (c) 2000, 2018, Oracle, MariaDB Corporation Ab and others. Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.
MariaDB [(none)]> use sampledb;
Drop table
MariaDB [books]> drop table authors; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.03 sec)
Verify table is dropped
MariaDB [books]> select * from authors; ERROR 1146 (42S02): Table 'books.authors' doesn't exist
At this point we have simulated a restore scenario, our data is gone!
Scale Deployment Config to 0
Before we can do a snapshot restore we need to shutdown the database by stopping the pod.
[ktenzer@keith-laptop ~]$ oc scale dc/mariadb --replicas=0 deploymentconfig.apps.openshift.io/mariadb scaled
Perform Snapshot Restore
To restore the snapshot we can use CSI provider or directly using the Ceph tools. Using the CSI provider will create a new PVC that is backed by the snapshot. In this case the snapshot will be cloned, thus creating a new read/write volume. Using the Ceph tools however we can rollback the snapshot without changing the underlying PV/PVC.
Snapshot Restore with CSI
$ vi restore-snapshot.yaml apiVersion: v1 kind: PersistentVolumeClaim metadata: name: mariadb-restore spec: storageClassName: ocs-storagecluster-ceph-rbd dataSource: name: mariadb-1 kind: VolumeSnapshot apiGroup: snapshot.storage.k8s.io accessModes: - ReadWriteOnce resources: requests: storage: 1Gi
$ oc apply -f restore-snapshot.yaml
Once new PVC is created, the deployment config needs to be updated to use the new volume.
$ oc edit cd/mariadb
---
volumes:
- name: mariadb
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: mariadb-restore
---
Snapshot Restore with Ceph Tools
Using the tools pod we can simply rollback the snapshot without creating a new PV/PVC.
$ oc rsh -n openshift-storage $TOOLS_POD rbd snap rollback ocs-storagecluster-cephblockpool/csi-vol-a380eb7b-021b-11ea-aa51-0a580a81000d@csi-snap-76040419-0228-11ea-aa51-0a580a81000d Rolling back to snapshot: 100% complete...done.
Scale Deployment Config to 1
After snapshot restore start database.
oc scale dc/mariadb --replicas=1 deploymentconfig.apps.openshift.io/mariadb scaled
Connect to database
[ktenzer@keith-laptop ~]$ oc rsh -n databases mariadb-6-rswv6
sh-4.2$ mysql -u root Welcome to the MariaDB monitor. Commands end with ; or \g. Your MariaDB connection id is 20 Server version: 10.2.22-MariaDB MariaDB Server Copyright (c) 2000, 2018, Oracle, MariaDB Corporation Ab and others. Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.
MariaDB [(none)]> use sampledb;
Show records for table authors.
MariaDB [books]> select * from authors; +------+-------+-----------------+ | id | name | email | +------+-------+-----------------+ | 1 | Keith | keith@domain.com| | 2 | John | john@domain.com | | 3 | Bob | bob@domain.com | +------+-------+-----------------+ 3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
The restore using our snapshot succeeded and as you can see our data is back...magic!
Summary
In this article we discussed how volume snapshots work and are implemented in kubernetes. Using OpenShift 4.2 and OpenShift Container Storage we demonstrated a backup and recovery of a mariadb database using volume snapshots in kubernetes. While it is early, this is a game changer for data workloads. Using volume snapshot we finally have a mechanism to integrate storage snapshots into kubernetes and as such provide proper backup and recovery solutions. I have no doubt this will lead to a large adoption of data workloads on kubernetes so get ready!
Happy Snapshotting!
(c) 2019 Keith Tenzer
